Question 1
A tied roof rafter is shown in the figure. Assumption: All required factors have been applied to the given load. The given load includes all imposed loads. The moment (ft-lb) at Point D in Member B-C is most nearly:
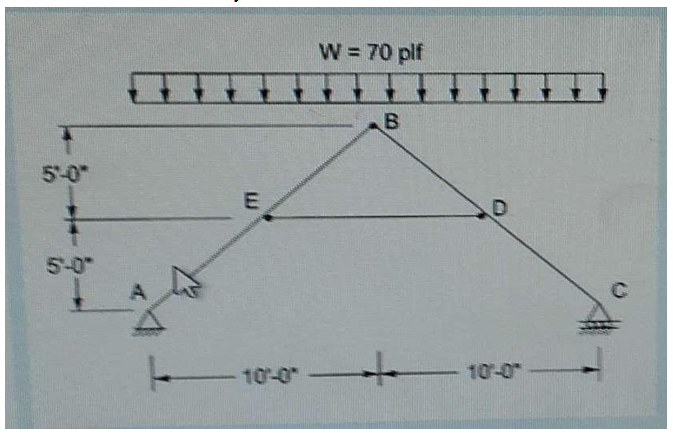
Correct Answer : c
Selected Answer : c
Explanation : uploads/Question_Image/f46084d1eb84a63eccb2f8aed710d2c51366518c.png
Explanation : 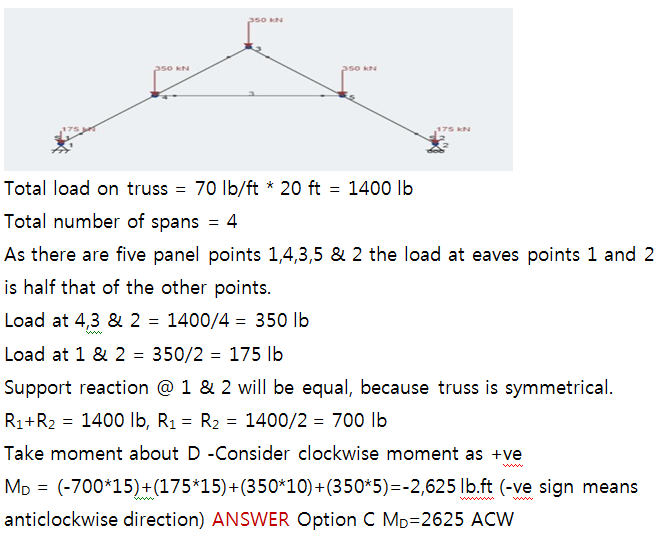
Question 2
In order to determine which basic hydraulic principles are applicable, a classification of flow is necessary. The flow condition at which the total energy head has a minimum value below which a given discharge cannot occur is termed:

Correct Answer : a
Selected Answer : a
Explanation : uploads/Question_Image/9de33fa9328efaf26251008045e030d1c80d1f79.png
Explanation : 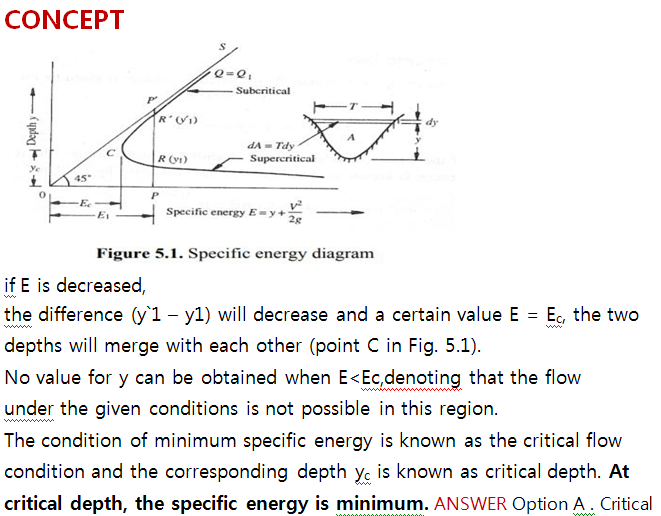
Question 3
The term fast track means

Correct Answer : b
Selected Answer : b
Explanation : CONCEPT Fast-track building construction is construction industry jargon for a project delivery strategy to start construction before the design is complete. The purpose is to shorten the time to completion. ANSWER Option B - Construction starts before the design is complete
Explanation : 
Question 4
Engineers are planning to place a shallow foundation as shown Engineers have decided that loose sand and soft clay are not capable of supporting the foundation without being treated what is the best.
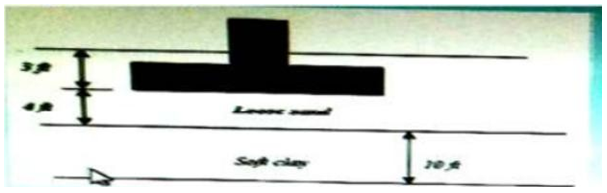
Correct Answer : b
Selected Answer : b
Explanation : CONCEPT (1) Pressure grouting or jet grouting involves injecting a grout material into otherwise inaccessible but interconnected pore or void space of which neither the configuration or volume are known, and is often referred to simply as grouting. The grout may be a cementitious, resinous, or solution chemical mixture. The greatest use of pressure grouting is to improve geomaterials (soil and rock). The purpose of grouting can be either to strengthen a formation or to reduce water flow through it. (2) Grouting in clay soils could easily result in an unsuccessful outcome because of a lack of good understanding of the rheological characteristics of grouts injected and the grout hose system. Additionally, for the purpose of lifting tilted building and/or structure, the dissipation of the excess porewater pressure generated during grout injection is likely to lead to a negative final compensation efficiency. (3) Dynamic compaction is suitable for densification of loose sand deposits. (4) Surcharge loading is suitable for clay -cohesive soil. (5) Vibro compaction is a ground improvement technique that densifies clean, cohesion less granular soils with a downhole vibrator. Hence to treat, Soft clay - Surcharge loading Loose sand - Dynamic compaction ANSWER Option B - B. Conduct dynamic compaction to treat loose sand and conduct surcharging to treat soft clay.
Explanation :  Pressure grouting or jet grouting involves injecting a grout material into otherwise inaccessible but interconnected pore or void space of which neither the configuration or volume are known, and is often referred to simply as grouting. The grout may be a cementitious, resinous, or solution chemical mixture. The greatest use of pressure grouting is to improve geomaterials (soil and rock). The purpose of grouting can be either to strengthen a formation or to reduce water flow through it. (2) Grouting in clay soils could easily result in an unsuccessful outcome because of a lack of good understanding of the rheological characteristics of grouts injected and the grout hose system. Additionally, for the purpose of lifting tilted building and/or structure, the dissipation of the excess porewater pressure generated during grout injection is likely to lead to a negative final compensation efficiency. (3) Dynamic compaction is suitable for densification of loose sand deposits. (4) Surcharge loading is suitable for clay -cohesive soil. (5) Vibro compaction is a ground improvement technique that densifies clean, cohesion less granular soils with a downhole vibrator. Hence to treat, Soft clay - Surcharge loading Loose sand - Dynamic compaction ANSWER Option B - B. Conduct dynamic compaction to treat loose sand and conduct surcharging to treat soft clay.)
Question 5
General conditions and home office overhead are examples of what type of costs?

Correct Answer : b
Selected Answer : b
Explanation : CONCEPT Overhead is indirect cost. Rent,Utilities & general office expenses are example of indirect cost. ANSWER Option B - Indirect
Explanation : 
Question 6
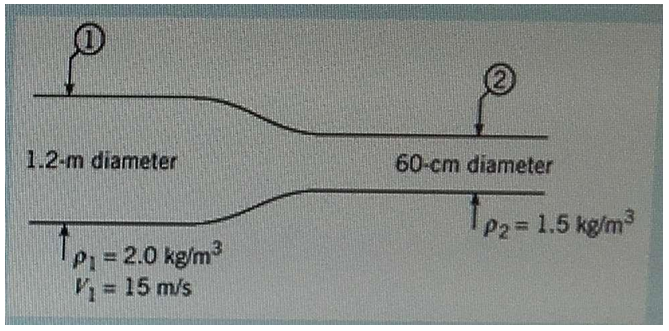
For the steady flow of gas in the conduit shown, what is the mean velocity at section 2?
Correct Answer : d
Selected Answer : d
Explanation : CONCEPT According to mass- continuity equation, 111 = 222 Where, A = Area ρ = Density V = Velocity GIVEN DETAILS At section 1 d1=Diameter = 1.2 m A1 = 2 = ∗ 1.22 = 1.35648 2 4 4 1 = Density=2 kg/m3 V 1= Velocity=15 m/s At section 2 D2=Diameter = 0.6 m A2 = 2 = ∗ 0.62 = 0.2826 2 4 4 2 = Density=1.5 kg/m3 V2= Velocity=?? SOLUTION 111 = 222 2 ∗ 1.35648 ∗ 15 = 1.5 ∗ 0.2826 ∗ 2 2 ∗ 1.35648 ∗ 15 = 1.5 ∗ 0.2826 = 80 / = ???? / ANSWER Option D .Velocity at section 2, 2 = 80 /
Explanation : 
Question 7
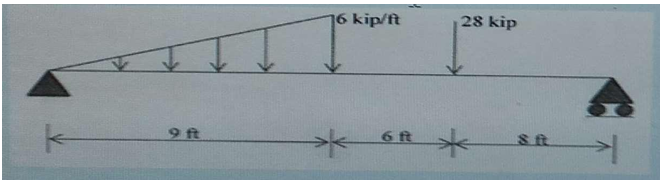
For the beam loaded as shown in the figure below, what is the location at which shear force is zero?
Correct Answer : d
Selected Answer : d
Explanation : SOLUTION Find support reactions Solve forces in Y direction Consider upward force as +ve ∑ = 0: + 1 ∑ = 0: − (6 ∗ 2 ∗ 9) − 28 = 0 1 + = (6 ∗ 2 ∗ 9) + 28 = 55 ???? + = 55 ???? Take moment about left support,A ∑ = 0 Consider clockwise moment as +ve − ∗ 23 + 28 ∗ 15 + 2 ∗ 9 ∗ 6 ∗ 3 ∗ 9 = 0 ∗ 23 = 28 ∗ 15 + 27 ∗ 6 = 28 ∗ 15 + 27 ∗ 6 23 = 25.30 + = 55 ???? = 55 − = 55 − 25.30 = 29.7 = 29.7 = 25.3 Consider section xx from left end A. SignconventiontodrawSFD SF at A, x=0 ft = 29.7 kips SF at C, x=9 ft = 29.7 - (0.5*6*9) =2.7 kipsSF at D+, x=15 ft = 29.7-(0.5*6*9) = 2.7 kips (Before reaching point load 28 kips) SF at D-, x=15 ft = 29.7-(0.5*6*9)-28=-25.3 kips (After reaching point load 28 kips) SF at B , x = 23 ft = 29.7-(0.5*6*9)-28=-25.3 kips = RB After checking SFD of given beam, we an understand that nowhere shear force is zero. At point load 28 kips, Shear force changes its sign from +ve to -ve. Hence we can say that at this point shear force is zero. ANSWER Option D - SF is zero @ 15 ft. from left support
Explanation :  − 28 = 0 1 + = (6 ∗ 2 ∗ 9) + 28 = 55 ???? + = 55 ???? Take moment about left support,A ∑ = 0 Consider clockwise moment as +ve − ∗ 23 + 28 ∗ 15 + 2 ∗ 9 ∗ 6 ∗ 3 ∗ 9 = 0 ∗ 23 = 28 ∗ 15 + 27 ∗ 6 = 28 ∗ 15 + 27 ∗ 6 23 = 25.30 + = 55 ???? = 55 − = 55 − 25.30 = 29.7 = 29.7 = 25.3 Consider section xx from left end A. SignconventiontodrawSFD SF at A, x=0 ft = 29.7 kips SF at C, x=9 ft = 29.7 - (0.5*6*9) =2.7 kipsSF at D+, x=15 ft = 29.7-(0.5*6*9) = 2.7 kips (Before reaching point load 28 kips) SF at D-, x=15 ft = 29.7-(0.5*6*9)-28=-25.3 kips (After reaching point load 28 kips) SF at B , x = 23 ft = 29.7-(0.5*6*9)-28=-25.3 kips = RB After checking SFD of given beam, we an understand that nowhere shear force is zero. At point load 28 kips, Shear force changes its sign from +ve to -ve. Hence we can say that at this point shear force is zero. ANSWER Option D - SF is zero @ 15 ft. from left support)
Question 8
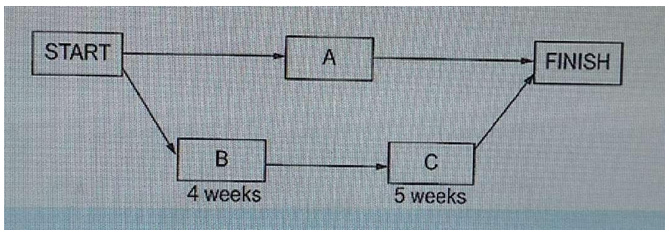
A contractor has scheduled work according to the network shown in the figure. Task A is performed by the contractor's employees and will take 4,000 labor hours of effort. The contractor has 10 laborers available to work this task at a standard 40 hr/week and 8 hr/day. Tasks B and C are both subcontracted and they have 4 weeks and 5 weeks, respectively, allocated in their subcontracts. Laborers cost $10/labor hour for straight time and $15/labor hour on overtime. The contractor estimates that it is possible to work 50 hr/week without impacting productivity. General conditions cost $1,000/day every day the contractor or subcontractors are on site. The optimal savings on working overtime is most nearly
Correct Answer : c
Selected Answer : c
Explanation : GIVEN DETAILS Total number of employees = 10 Nos Total labor hours = 4000 hours Working hours/day = 8 hrs/day Total number of working days in a week = 5 days Labor cost = $ 10 / labor/hour General condition cost per day = $ 1000 Over time Total number of employees = 10 Nos Total labor hours = 4000 hours Total number of working hours in a week = 50 hrs/week Total number of working days in a week = 5 days Working hours/day = 10 hrs/day Labor cost = $ 15 / labor/hour General condition cost per day = $ 1000 SOLUTION Total labor hours = 4000 hours Working hours/day = 8 hrs/day Number of days required to complete 4000 labor hours = 4000 ℎ???? = 8 ℎ???? ???? = 500 ???? Numberofdaysrequiredtocomplete4000laborhours=500days Total number of labors required for 1 day work = 10 labors Labor cost = $ 10 / labor/hour Total labor cost per day = 10 labors ∗ $10/labor/hour ∗ 8 hours = $800 Totallaborcostperday=$800/day Number of days required to complete 4000 labor hours = 500 days Total labor cost for 500 days = 500 days * $800/day = $ 400 000 Total labor cost for 500 days = $ 400 000 General condition cost per day = $ 1000 Total General condition cost for 500 days = 500 days * $1000/day = $ 500 000 Total General condition cost for 500 days = $ 500 000 Total cost for 500 days = total labor cost + total general condition cost =$ 400 000 + $ 500 000 = $ 900 000 Total cost for 500 days = $ 900 000 OVERTIME Total labor hours = 4000 hours Working hours/day = 10 hrs/day Working hours can be split into 2 categories Regular work = 8hrs/day Overtime = 2 hrs/day Number of days required to complete 4000 labor hours = 4000 ℎ???? = 1 0ℎ ???? ???? = 400 ???? Numberofdaysrequiredtocomplete4000laborhours=400days Total number of labors required for 1 day work = 10 labors Labor cost = $ 15 / labor/hour (OVERTIME) - 2hrs/day Labor cost = $ 10 / labor/hour (REGULAR) - 8hrs/day Total labor cost per day = (10 labors ∗ $15/labor/hour ∗ 2 hours) + 10 labors ∗ $10/labor/hour ∗ 8 hours = $300 + $800 = $1100 Totallaborcostperday=$1100/day Number of days required to complete 4000 labor hours = 400 days Total labor cost for 400 days = 400 days * $1100/day = $ 44 00 00 Total labor cost for 500 days = $ 44 00 00 General condition cost per day = $ 1000 Total General condition cost for 500 days = 400 days * $1000/day = $ 40 00 00 Total General condition cost for 500 days = $ 40 00 00 Total cost for 500 days = total labor cost + total general condition cost =$ 44 00 00 + $ 40 00 00 = $ 84 00 00 Total cost for 500 days = $ 840 000 Regular Total cost = $900 000 Over time Total cost = $840 000 Savings = $900 000 - $840 000 = $ 60 000 For 1 labor = $60000/10 = $6000 ANSWER Option C - Optimal savings = $ 6000
Explanation :  - 2hrs/day Labor cost = $ 10 / labor/hour (REGULAR) - 8hrs/day Total labor cost per day = (10 labors ∗ $15/labor/hour ∗ 2 hours) + 10 labors ∗ $10/labor/hour ∗ 8 hours = $300 + $800 = $1100 Totallaborcostperday=$1100/day Number of days required to complete 4000 labor hours = 400 days Total labor cost for 400 days = 400 days * $1100/day = $ 44 00 00 Total labor cost for 500 days = $ 44 00 00 General condition cost per day = $ 1000 Total General condition cost for 500 days = 400 days * $1000/day = $ 40 00 00 Total General condition cost for 500 days = $ 40 00 00 Total cost for 500 days = total labor cost + total general condition cost =$ 44 00 00 + $ 40 00 00 = $ 84 00 00 Total cost for 500 days = $ 840 000 Regular Total cost = $900 000 Over time Total cost = $840 000 Savings = $900 000 - $840 000 = $ 60 000 For 1 labor = $60000/10 = $6000 ANSWER Option C - Optimal savings = $ 6000)
Question 9
A 112-in-diameter, 7-wire pre stressing strand is to be stressed in the pre tensioning bed shown with a jacking force of 14 tons of the live-end hydraulic jack is 310ft. For the strand properties indicated, the expected strand elongation (in.) is most nearly

Correct Answer : d
Selected Answer : d
Explanation : uploads/Question_Image/656d0b7d04aee51f5e338151d034e5336cfe0b1e.png
Explanation : 
Question 10
The moisture content of timber used in building frames can be

Correct Answer : b
Selected Answer : b
Explanation : CONCEPT Moisture content of timber for indoor use -8-14% Moisture content of timber for outdoor use -12%-18% ANSWER Option B -8% to 12%
Explanation : 
Question 11
The power (ft-lb/sec) that must be imparted to 1 MGD of water passing through a rapid mix unit (given a water temperature of 50 o F and a velocity gradient of 700 sec-?) is :

Correct Answer : b
Selected Answer : b
Explanation : uploads/Question_Image/8c2d0620e698c3f1643d2bd2672a406c3ba6ca7e.png
Explanation : 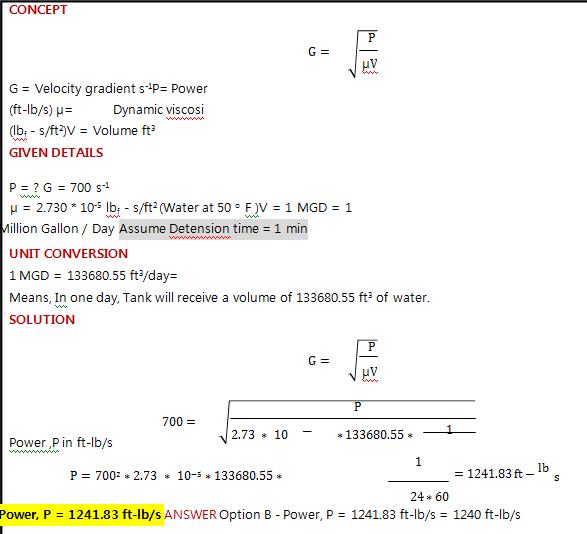
Question 12
The intersection of the WBS and the OBS is the:

Correct Answer : c
Selected Answer : c
Explanation : uploads/Question_Image/7e5ea528c7ebe17defc7fe66a4d98c62ad530640.png
Explanation : 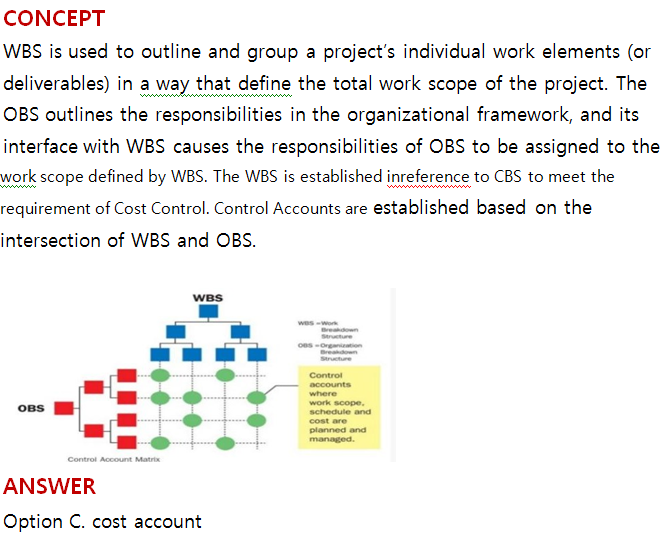
Question 13
The molar concentration of water is:

Correct Answer : b
Selected Answer : b
Explanation : CONCEPT The standard state for a liquid is the pure liquid, so the standard state of water is pure water, whose concentration is 55.5 M (in a liter, there are 55.5 moles of water, so its concentration is 55.5 mol/L). ANSWER Option B Molar concentration of water = 55.6 mole/L
Explanation : . ANSWER Option B Molar concentration of water = 55.6 mole/L)
Question 14
If a specification is in conflict with a note on the drawings, which statement is correct?

Correct Answer : c
Selected Answer : c
Explanation : CONCEPT If a specification is in conflict with a note on the drawings, then Specifications take precedence over drawings. ANSWER Option C .Specifications take precedence over drawings.
Explanation : 
Question 15
The figure shows the loads acting on a beam. The shear diagram is most nearly
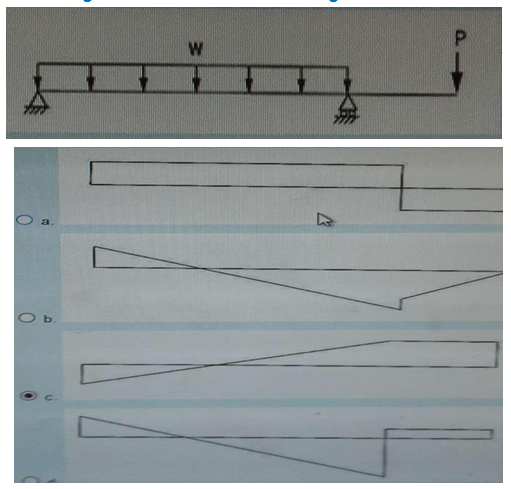
Correct Answer : d
Selected Answer : d
Explanation : uploads/Question_Image/d1c7ba9fe43129b6edddd2b2c8604ad8f1a8b658.png
Explanation : 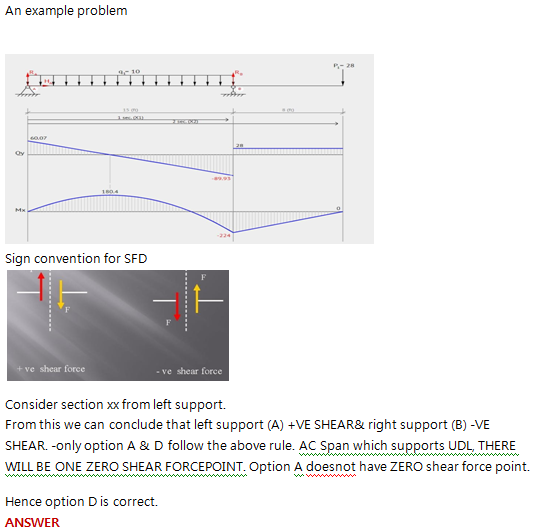
Question 16
The slope at C (the mid-span of the beam) for the beam shown below is:

Correct Answer : a
Selected Answer : a
Explanation : uploads/Question_Image/0fadb37b5473a89229bfd37dabdd7eb3b9307622.png
Explanation : 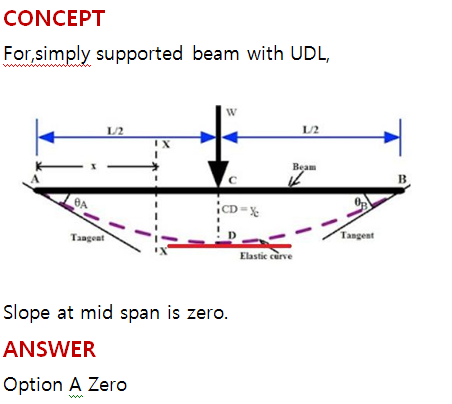
Question 17
ABET stands for Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology

Correct Answer : a
Selected Answer : a
Explanation : CONCEPT ABET - Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology ANSWER Option A - True
Explanation : 
Question 18
The advantages of a Design/Bid/Build contractual arrangement is (are).

Correct Answer : b
Selected Answer : c
Explanation : CONCEPT Design-bid-build is the traditional low bidder model and is one of the most popular delivery methods. With this approach, the project owner establishes separate contractual relationships with the design team (architect and engineer) and the general contractor (GC) who will perform the construction activities. The method is straightforward enough for homeowners to stay on top of and understand. Unlike the design-build delivery, there is less collaboration between the design team and the GC, and thus design changes are easier to track. Owners can be fully engaged in the design process, while the design team and the contractor’s roles are more autonomous, and the responsibilities of each function are better defined. ANSWER Option B & C are correct- B. Non-adversary relationships among participants C. Known project cost before construction
Explanation :  and the general contractor (GC) who will perform the construction activities. The method is straightforward enough for homeowners to stay on top of and understand. Unlike the design-build delivery, there is less collaboration between the design team and the GC, and thus design changes are easier to track. Owners can be fully engaged in the design process, while the design team and the contractor’s roles are more autonomous, and the responsibilities of each function are better defined. ANSWER Option B & C are correct- B. Non-adversary relationships among participants C. Known project cost before construction)
Question 19
Resource leveling usually results in:

Correct Answer : c
Selected Answer : c
Explanation : uploads/Question_Image/24a986ea82e85c833f396b73991d45f00880be0e.png
Explanation : 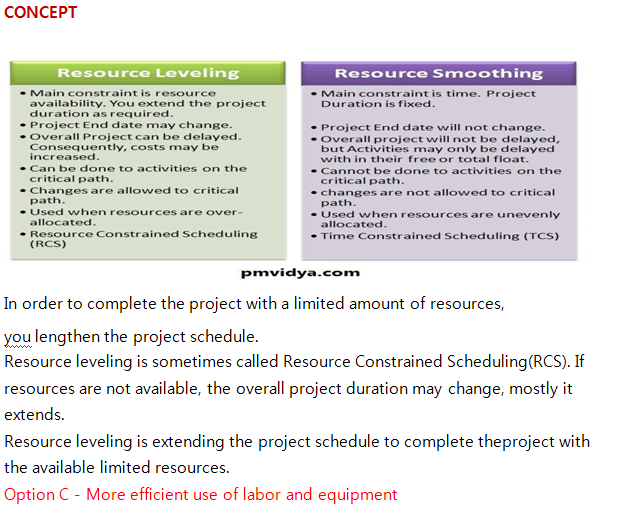
Question 20
Consider the following characteristics regarding timber. 1. Stronger variety 2. Ability to take very smooth finish 3. Toughness 4. Difficult to season Which of the above characteristics is/are essential for timber to be used as beams?

Correct Answer : d
Selected Answer : d
Explanation : CONCEPT QUALITIES OF GOOD TIMBER STRENGTH It should have sufficient strength to resist heavy structural loads. TOUGHNESS It should have enough toughness to resist shocks due to vibrations. It should not break in bending and should resist splitting. Timbers having narrow annual rings, are generally the strongest. WORKABILITY It should be well seasoned and easily workable. Teeth of saw should not get clogged during the process of sawing. It should provide smoothened surface easily. Ability to take very smooth finish is also an important factor. OPTION - 1 & 3 most suitable options. ANSWER Option D - 1& 3
Explanation : 
Question 21
Structures are most sensitive to:

Correct Answer : b
Selected Answer : b
Explanation : CONCEPT Uneven settlement of the soil beneath the foundation of a structure that may lead to “sinking” of different parts of the structure which causes cracks and other structural problems. ANSWER Option B. Differential settlement
Explanation : 
Question 22
The slump test used for

Correct Answer : a
Selected Answer : a
Explanation : CONCEPT It is performed to check the workability of freshly made concrete, and therefore the ease with which concrete flows. ANSWER Option - A -Workability
Explanation : 
Question 23
The factors that govern the workability of fresh concrete are?

Correct Answer : d
Selected Answer : d
Explanation : CONCEPT Factors affecting workability of concrete 1. Water content 2. Water -Cement ratio 3. Size of aggregate 4. Admixture 5. Texture 6. Grading of aggregate 7. Cement-Aggregate ratio 8. Transportation time 9. Aggregate Cement ratio 10. Cement paste plasticity or consistency of cement paste or easiness to mold ANSWER Option D - All the above
Explanation : 
Question 24
Which of the following situations requires a change order?

Correct Answer : d
Selected Answer : d
Explanation : CONCEPT In project management, change orders are also called variations or variation orders. Any modification or change to works agreed in the contract is treated as a variation. These modifications can be divided into three main categories 1. Addition to the work agreed in the contract. 2. Omission of work agreed in the contract. 3. Substitution or alteration of work agreed in the contract. A change order is work that is added to or deleted from the original scope of work of a contract, however, depending on the magnitude of the change, it may or may not alter the original contract amount and/or completion date. A change order may force a new project to handle significant changes to the current project. Change orders are common to most projects, and very common with large projects. After the original scope (or contract) is formed, complete with the total price to be paid and the specific work to be completed, a client may decide that the original plans do not best represent his or her definition for the finished project. Accordingly, the client will suggest an alternate approach. Common causes for change orders to be created are: The project's work was incorrectly estimated The customer or project team discovers obstacles or possible efficiencies that require them to deviate from the original plan The customer or project team are inefficient or incapable of completing their required deliverables within budget, and additional money, time, or resources must be added to the project During the course of the project, additional features or options are perceived and requested. If the contractor has to add work items to the original scope of work at a later time in order to achieve the customer's demands, a fair price for the work items and fees must be added for the materials and labor. ANSWER Option D - All the above
Explanation :  is formed, complete with the total price to be paid and the specific work to be completed, a client may decide that the original plans do not best represent his or her definition for the finished project. Accordingly, the client will suggest an alternate approach. Common causes for change orders to be created are: The project's work was incorrectly estimated The customer or project team discovers obstacles or possible efficiencies that require them to deviate from the original plan The customer or project team are inefficient or incapable of completing their required deliverables within budget, and additional money, time, or resources must be added to the project During the course of the project, additional features or options are perceived and requested. If the contractor has to add work items to the original scope of work at a later time in order to achieve the customer's demands, a fair price for the work items and fees must be added for the materials and labor. ANSWER Option D - All the above)
Question 25
The following relationship means

Correct Answer : d
Selected Answer : d
Explanation : ANSWER Option D -Activity B has to start at least 2 days before the completion of activity A
Explanation : 
Question 26
How many types of fine aggregates are there based on source?

Correct Answer : a
Selected Answer : a
Explanation : Three types are natural sand (river banks), crushed stone sand (hard stone) and crushed gravel sand (gravel).
Explanation : , crushed stone sand (hard stone) and crushed gravel sand (gravel).)
Question 27
An ideal fluid is

Correct Answer : b
Selected Answer : b
Explanation :
Explanation : 